System Design Notes
I found these notes sometime ago, i am not the author.
-
Try to break th problem into simple modules (Top Down approach)
-
Talk about the trade-off (No soltion is perfect) Calculate the impact on system based on all the constraints and the end test cases
-
Architectural pieces/resources available
-
How these resources work together
-
Utilization and Tradeoffs
- Consistent Hashing
- CAP Theorem
- Load balancing
- Type of distribution
- Random
- Round-robin
- Weight for CPU & Memory cycle
- To utilize full scalabillity & redundancy(Add 3 LB[3-Tier Architecutre])
- User « LB1 » Web Server
- Web Server « LB2 » App Server / Cache Server
- App Server / Cache Server « LB3 » DB
- Smart Clients
- Takes a pool of service hosts & balances load
- detects hosts that are not responsive
- recovered hosts
- addition of new hosts
- Load balancing functionality to DB(Cache service)
- Attractive solution for developers
- As system grows > LBs (Standalone Servers)
- Takes a pool of service hosts & balances load
- Hardware Load Balancers
- Expensive but high preformance
- Not trivial to configure
- Large companies tond to avoid this config or use it as 1st point of contact to their system to serve user requests
- Intra network uses smart clients / hybrid solution for load balancing traffic
- Software Load Balancers
- No pain of creation of smart client
- No cost of purchasing dedicated hardware
- hybrid approach : HAProxy(OSS Load balancer)
- Running on client machine(Client managed by HAProxy)
- Running on intermediate server(Server Side Components)
- HAProxy
- manages health checks
- removal & addtion of machines
- balances requests a/c pools
- Type of distribution
- Queues
- effectively manages requests in large-scal distubuted system
- In small systems > write are fast
- In complex systems > high incomming load & individual write take mass time
- To achieve high performance & availaility (System need to the asynchronous > Queues)
- difficult for fair & balanced distribution
- Caching
- Replication
- SQL vs No-SQL
- SQL(Relational Database)
- Structured
- Predefined schema
- Data in rows & columns
- MySQL, Oracle, MS SQL Server, SQLite, Postgre, MariaDB
- NO SQL(Non Relational Dataase)
- Unstructured
- distributed
- dynamic schema
- DB Method: Key-Value Stores, Document DB, Wide-column DB, Graph DB
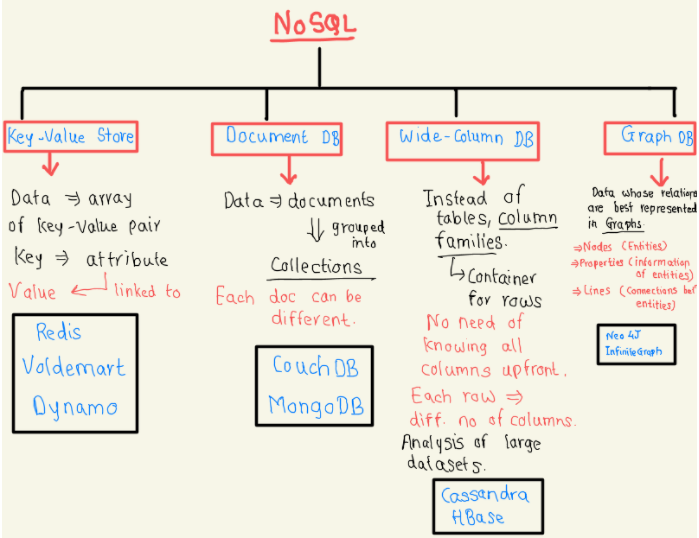
- High Level differences between SQL & NoSQL | Property | SQL | NoSQL | |—|—|—| |A|B|C|
- SQL(Relational Database)
- Indexes
- Proxies
- Data Partitioning
 Blueseam
Blueseam 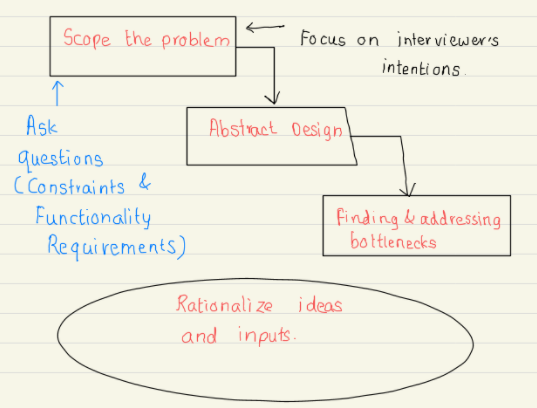
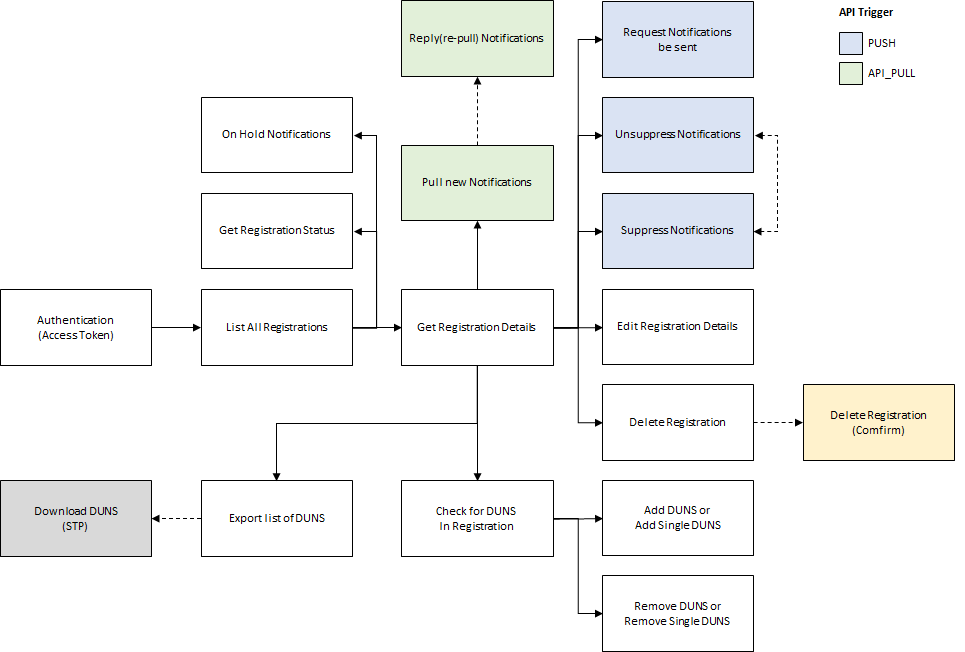 Direct Plus Monitor API Service Flow
Direct Plus Monitor API Service Flow